Abstract

Background: Hematological toxicity and concomitant infectious complications drive the toxicity burden of CD19 CART. We recently proposed a classification system for CART-related hematotoxicity, defining three unique phenotypes of hematopoietic recovery (Rejeski et al, Blood 2021). The underlying mechanisms of these phenotypes and their relation to survival remain poorly understood. Here, we sought to understand patterns of post-CART neutrophil recovery and their influence on clinical outcomes.
Methods: In this multicenter retrospective study, we analyzed 344 pt. receiving standard-of-care axi-cel (n=208) or tisa-cel (n=136) for R/R LBCL. The phenotypes of neutrophil recovery were defined as follows:
Quick: sustained neutrophil recovery without a second dip below an ANC<1000/µl.
Intermittent: neutrophil recovery (ANC>1500/µl) followed by a second dip with an ANC<1000/µl after day 21.
Aplastic: continuous severe neutropenia (ANC<500/µl) ≥14 days.
Multivariate analysis of patient-, disease-, and therapy-related factors was performed as binary logistic regression for the aplastic vs. non-aplastic phenotypes. Variables with a p<0.2 on univariate analysis were included. Clinical outcomes were studied via Kaplan-Meier estimates.
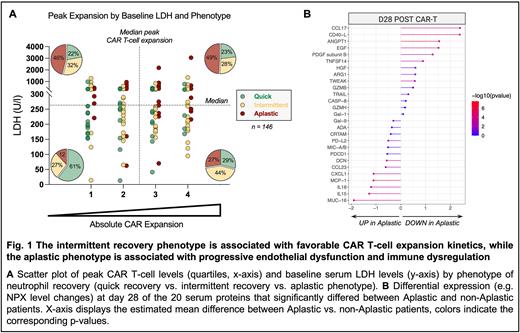
Quantification of CAR T-cells was performed by qPCR or by flow cytometry in 146 pt. according to institutional protocols. To harmonize CAR T-cell expansion across centers, patients were divided into quartiles by their respective peak expansion. Plasma proteomics were performed in 56 pts. across four time points (day 0, 4, 14, 28) using a 92-protein multiplex proximity extension assay (Olink Proteomics). Key candidate serum markers were validated in 70 pt. using the Ella automated immunoassay system (ProteinSimple).
Results: Across all patients, the distribution of the 'aplastic' (A), 'intermittent' (I) and 'quick' (Q) phenotypes was 18%, 42%, and 40%, respectively. The 'aplastic' patients exhibited a longer median duration of severe neutropenia, (A vs. I vs. Q: 26 vs. 10 vs. 5 days, p<0.001), a higher rate of severe infections (A vs. I vs. Q: 41% vs. 23% vs. 18%) and a trend towards higher 1-year non-relapse mortality (A vs. I: 9% vs. 3.5%, p=0.08).
On multivariate regression (n=344), the aplastic phenotype was independently associated with the presence of BM infiltration (adjusted OR=3.2, p=0.004), ANC (aOR=0.28, p=0.002), and ferritin (aOR=2.3, p=0.039). Neither high-grade CRS or ICANS nor CAR product were linked to the aplastic phenotype. In the 'intermittent' cohort, we noted a significant decrease of both serum ferritin (median 776 vs. 321 U/L) and CRP levels (median 1.6 vs. 0.2 mg/dL) between CAR infusion and day 90 follow-up.
When studying CD3+ CAR T-cell dynamics over time, we found that patients with 'intermittent' recovery displayed both an earlier and more pronounced expansion peak, and longer CART persistence compared to their 'quick' counterparts. While the 'aplastic' cohort displayed comparable peak CART expansion, these patients also exhibited high baseline LDH, indicative of a higher baseline tumor burden, or 'hill to climb' (top right quadrant, Fig. 1A). Conversely, the 'quick' cohort was characterized by both low expansion and low LDH. Serum proteome analysis revealed significant disruptions of endothelial function and immune dysregulation in the 'aplastic' patients at month 1 (Fig. 1B). Importantly, we confirmed higher peak IFNγ and IL-15 levels, and an increased ratio of ANG2 to ANG1 in the 'aplastic' patients in the independent validation cohort.
Notably, progression-free (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was poor in the 'aplastic' patients (1-yr PFS 26%, 1-yr OS 46%). On the other hand, 'intermittent' patients exhibited the best survival outcomes (HRPFS I vs. A: 0.45, 95% CI 0.31-0.65). Median PFS was 3 vs. 20 vs. 4 months (A vs. I vs. Q, p<0.001); median OS was 8 months vs. not-reached vs. 23 months (A vs. I vs. Q, p<0.001).
Conclusion: The 'aplastic' phenotype is driven by baseline inflammation and hematopoietic function, characterized by progressive endothelial dysfunction, and associated with poor PFS/OS. In contrast, the 'intermittent' phenotype (i.e. biphasic cytopenia) was associated with high levels of CART expansion and persistence, a decrease in systemic inflammation over time, and excellent survival outcomes. Overall, these data suggest potential interactions between host hematopoiesis and CART function and efficacy.
Disclosures
Rejeski:Novartis: Honoraria; Kite/Gilead: Other: Travel Support, Research Funding. Iacoboni:NOVARTIS, KITE/GILEAD, BMS/CELGENE, ASTRAZENECA, ROCHE, ABBVIE, JANSSEN, MILTENYI: Honoraria; NOVARTIS, KITE/GILEAD, BMS/CELGENE: Consultancy. Buecklein:Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Miltenyi Biotech: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria; Pfizer: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Honoraria. Blumenberg:Celgene: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding. Penack:Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MSD: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shionogi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; SOBI: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Research Funding; Priothera: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Jazz: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Omeros: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Therakos: Honoraria; Equillium Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria. Faramand:Kite/Gilead: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding. Locke:ASH: Other: Education or editorial activity; BioPharm Communications: Other: Education or editorial activity; CAREducation: Other: Education or editorial activity; Clinical Care Options Oncology: Other: Education or editorial activity; Imedex: Other: Education or editorial activity; Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer: Other: Education or editorial activity; CERo Therapeutics: Research Funding; Sana: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Aptitude Health: Other: Education or editorial activity; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; ), National Cancer Institute: Research Funding; Leukemia and Lymphoma Society: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; A2: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Other: Patents & Royalties: patents, royalties, other intellectual property from several patents held by the institution in my name (unlicensed) in the field of cellular immunotherapy.; Wugen: Consultancy; Umoja: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Legend Biotech: Consultancy; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Iovance: Consultancy; GammaDelta Therapeutics: Consultancy; Emerging Therapy Solutions Gerson Lehrman Group: Consultancy; EcoR1: Consultancy; Cowen: Consultancy; Calibr: Consultancy; Cellular Biomedicine Group: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene: Consultancy; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy, Research Funding; Allogene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy. Bullinger:Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene/BMS: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bayer Oncology: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Mackensen:BMS/Celgene: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Kite/Gilead: Honoraria; Miltenyi Biomedicine: Honoraria. Barba:Allogene, Amgen, BMS, Gilead, Incyte, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Miltenyi Biomedicine, Nektar and Novartis: Consultancy. Jain:Incyte: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy; MyeloidTx: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding. Subklewe:Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Seagen: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Miltenyi Biotech: Research Funding; Takeda: Other: Travel support; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Morphosys: Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.